Lloyds of London, the insurance market, and Chatham House have published a white paper on Sustainable Energy Security that details the risks and opportunities for business.
Lloyd’s CEO, Dr. Richard Ward, doesn’t mince words in his foreword to the white paper:
This report, jointly produced by Lloyd’s 360 Risk Insight programme and Chatham House, should cause all risk managers to pause. What it outlines, in stark detail, is that we have entered a period of deep uncertainty in how we will source energy for power, heat and mobility, and how much we will have to pay for it.
Is this any different from the normal volatility of the oil or gas markets? Yes, it is. Today, a number of pressures are combining: constraints on ‘easy to access’ oil; the environmental and political urgency of reducing carbon dioxide emissions; and a sharp rise in energy demand from the Asian economies, particularly China.
All of this means that the current generation of business leaders – and their successors – are going to have to find a new energy paradigm. Expect dramatic changes:
- Prices are likely to rise, with some commentators suggesting oil may reach $200 a barrel.
- Regulations on carbon emissions will intensify.
- Reputations will be won or lost as the public demands that businesses reduce their environmental footprint.
The growing demand for energy will require an estimated $26 trillion in investment by 2030. Energy companies will face hard choices in deciding how to deploy these funds in an uncertain market with mixed policy messages. The recent Deepwater oil spill shows all too clearly the hazards of moving into ever more unpredictable terrain to extract energy resources. And the rapid deployment of cleaner energy technologies will radically alter the risk landscape. At this precise point in time we are in a period akin to a phony war. We keep hearing of difficulties to come, but with oil, gas and coal still broadly accessible – and largely capable of being distributed where they are needed – the bad times have not yet hit. The primary purpose of this report is to remind the reader that all businesses, not just the energy sector, need to consider how they, their suppliers and their customers will be affected by energy supplies which are less reliable and more expensive.
The failure of the Copenhagen Summit has not helped to instil a sense of urgency and it has hampered the ability of businesses – particularly those in the energy sector – to plan ahead and to make critical new investments in energy infrastructure. I call on governments to identify a clear path towards sustainable energy which businesses can follow.
Independently of what happens in UN negotiating rooms, businesses can take action. We can plan our energy needs, we can make every effort to reduce consumption, and we can aim for a mix of different energy sources. The transformation of the energy environment from carbon to clean energy sources creates an extraordinary risk management challenge for businesses. Traditional models that focus on annual profits and, at best, medium term strategies may struggle. Parts of this report talk about what might happen in 2030 or even 2050 and I make no apology for this. Energy security requires a long term view and it is the companies who grasp this who will trade on into the second half of this century.
Executive Summary
- Businesses which prepare for and take advantage of the new energy reality will prosper – failure to do so could be catastrophic.
- Market dynamics and environmental factors mean business can no longer rely on low cost traditional energy sources.
- China and growing Asian economies will play an increasingly important role in global energy security
- We are heading towards a global oil supply crunch and price spike.
- Energy infrastructure will become increasingly vulnerable as a result of climate change and operations in harsher environments.
- Lack of global regulation on climate change is creating an environment of uncertainty for business, which is damaging investment plans.
- To manage increasing energy costs and carbon exposure businesses must reduce fossil fuel consumption.
- Business must address energy-related risks to supply chains and the increasing vulnerability of ‘just-in-time’ models.
- Investment in renewable energy and ‘intelligent’ infrastructure is booming. This revolution presents huge opportunities for new business partnerships.
A change in the energy market balance between East and West
Advanced economies remain the biggest consumers of primary energy per person but by 2008 non-OECD countries led by China and India had outstripped them in terms of the share of world demand. This shift began in the 1990s, partly because manufacturing shifted eastwards. Meanwhile, lower population growth, de- industrialisation, greater efficiency, higher fuel prices and a concern for the environment are lowering demand for oil-based fuels and coal in the OECD.
These consumption trajectories mean there is likely to be a tipping point in 2015 when countries in Asia-Pacific need more imported oil in total than the Middle East (including Sudan) can export.
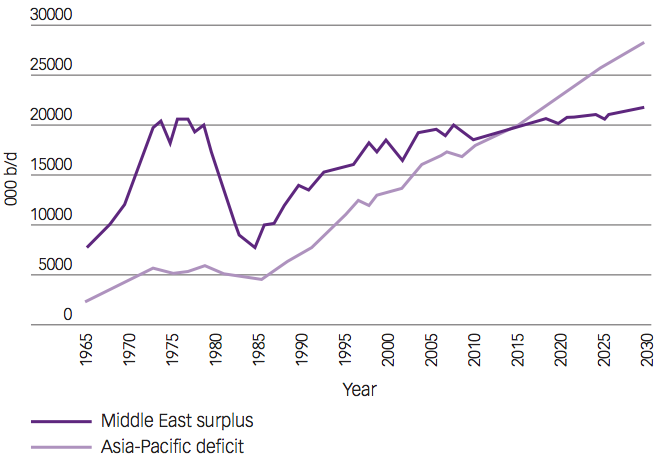
The white paper goes on to detail market forces, energy trends, risk and opportunity. This is recommended reading for business and government leaders and risk managers.
0 thoughts on “Sustainable Energy Security: Strategic Risks and Opportunities for Business”
Comments are closed.