At a recent Crossroads Lecture, energy policy expert Daniel Kammen spoke about Energizing the Low-Carbon Future. His presentation is timely – climate change has been on the public mind as hurricane superstorm Sandy devastated New York, New Jersey, and beyond. Though we would all agree that energy is an essential part of our daily life, Americans spend more money on potato chips than on energy research and development. Dan has a deep nuanced understanding of where we are at, and where we need to go, to build a clean, sustainable energy future.
In the presentation below, Dr. Kammen explores innovations in, and barriers to, building renewable energy systems worldwide – from villages to large regional economies. He discusses tools already available, and others needed, to speed the transition to a sustainable planet. Daniel Kammen is Professor in the Energy and Resources Group (ERG), Professor of Public Policy in the Goldman School of Public Policy at the University of California, Berkeley. He is also the founding Director of the Renewable and Appropriate Energy Laboratory (RAEL). Kammen advises the World Bank, and the Presidents Committee on Science and Technology (PCAST), and is a member of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (Working Group III and the Special Report on Technology Transfer).
Dan spoke for about an hour, followed by a 35 minute question and answer session. The Q&A session has some great questions and discussion.
Dan talked about cleantech jobs, the economic benefits of transitioning to renewable energy, climate change, coal, natural gas, arctic sea ice loss, peak oil, the real cost of coal and other high-carbon sources of energy, solar energy, and energy storage. One of my favorite quotes:
When you are spending your funds buying fuels as a fraction of the cost of the technology, it’s a very different equation than when you are investing in people, training, new companies, and intellectual capital. [And so, for example] if you buy a gas turbine, 70 percent of the money that will go in to that, over its lifetime, is not going to be for human resources and hardware, it’s to buy fuel. If you buy renewable energy and energy efficiency, while we have a problem of needing to find ways to amortize up-front costs, you are investing in people, companies, and innovation.
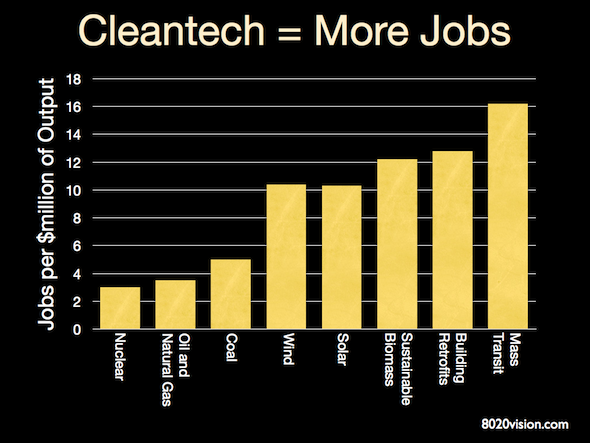
Jobs created, per dollar invested, are consistently higher for cleantech jobs versus old fossil fuel based energy sources. Economist Robert Solow, in his Nobel prize winning work on the drivers of economic growth, demonstrated that about 75 to 80 percent of the growth in US output per worker was attributable to technical progress and innovation. Transitioning to renewable forms of energy will provide strong stimulus to our economy, while reducing public health and environmental costs associated with dirty coal and oil pollution.
After Dan Kammen finished overviewing climate change and energy issues, he highlighted several case studies that featured renewable energy and low-carbon energy production implementations for small (personal), medium (community) and large (national) installations. Watch the video above for more.
Recommended Reading